The sun, our greatest energy body in the sky, is driving the revolution of renewable energies worldwide. Spain and Australia are at the forefront of this development, albeit with different approaches. While Spain aims for a combination of photovoltaic and concentrated solar power plants, Australia largely relies on photovoltaics. These differences affect not only the efficiency of energy production but also the type of infrastructure and governmental support. Each of these aspects offers valuable insights for investors and individuals looking to invest in the growing solar market.
The Worship of the Sun: How Technologies Shape Solar Energy Efficiency in Spain and Australia

The issue of solar energy efficiency in Spain and Australia is closely linked to the technological solutions used in both countries for energy production. These solutions are directly related to climatic conditions, technologies, and the political context.
Climatic conditions play a decisive role in solar energy efficiency. Australia, as one of the sunniest nations in the world, intensely harnesses this natural resource. Regions such as Western Australia and the Northern Territory benefit from almost constantly high solar irradiation, optimizing the efficiency of solar plants. In comparison, Spain, despite its high sunlight hours, especially in the Andalusia region, has slightly lower radiation values. This difference minimally affects the energy performance of solar plants but remains a noteworthy factor.
Technological developments underscore the differences between the two countries. Spain distinguishes itself through its extensive use of Concentrated Solar Power (CSP). This technology allows not only for electricity production during the day but also for energy storage to ensure reliable supply after sunset. Thus, CSP broadens the scope of solar energy, offering baseload capacity, which strengthens the system’s recurring reliability. In contrast, Australia has made significant progress in photovoltaics (PV). The high efficiency of modern PV systems, supported by innovative technologies such as heterojunction technology, makes this form of solar energy particularly attractive. PV is not only easier to install and maintain but also ideal for decentralized energy supply.
Besides the purely technological aspects, political conditions and funding play a fundamental role. Currently, Australia is experiencing a political push towards renewable energies, driven by government funding programs and increasing public demand. A similar proactive attitude can be observed in Spain, where solar parks are growing thanks to both political measures and investment incentives. This government support ensures that solar energy remains a central component in the energy transition of both countries.
The effects on energy production are clear: both countries have developed enormous capacities, with Australia potentially boasting a slight advantage in efficiency due to its high solar irradiation rates. At the same time, the technological variety in Spain with CSP offers the possibility to ensure a constant energy supply, even when the sun is less available.
Both Spain and Australia are at the forefront of solar energy innovation. While Australia maximizes the power of the sun through innovative PV technologies, Spain combines traditional PV methods with the promising possibilities of CSP plants. This strategic and technological network makes both countries benchmark examples for the efficient use of solar energy globally.
Spain vs Australia: The Development of Solar Energy Infrastructure and Government Support
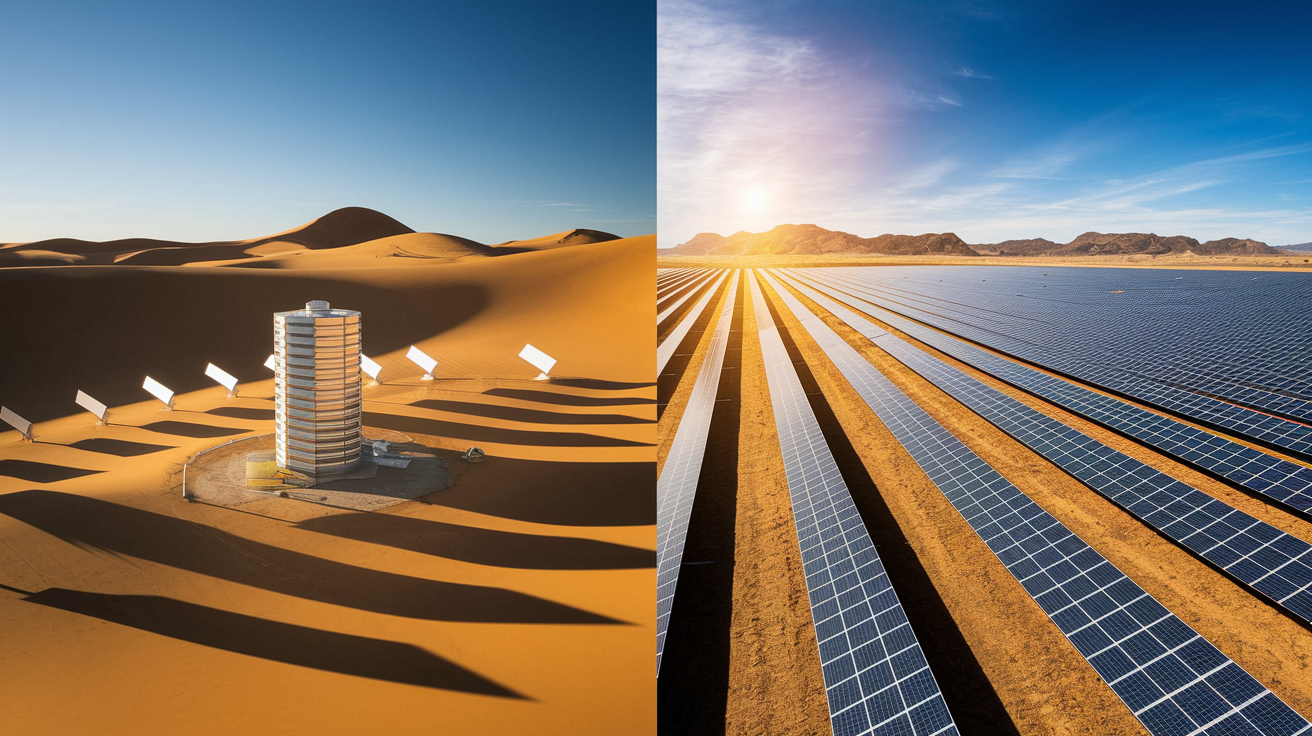
Spain and Australia are both pioneers in the use of solar energy technologies, but their approaches to infrastructure development and capacity expansion differ significantly. In this chapter, we will take a closer look at the unique developments in both countries as well as the government measures that promote them.
In Spain, solar energy has seen significant development in recent years. Installed photovoltaic power increased from 30 GW in 2022 to an impressive 39 GW in 2023. This progress is largely due to significant solar projects and the country’s clear political objectives. The Spanish government has expressed ambitious plans to increase the share of renewable energies to 39% by 2030, supported by incentive programs such as feed-in tariffs and investment incentives. Such incentives are crucial for promoting the necessary integration into the power grid, a challenge that persists despite the success story.
Australia follows a different but equally successful path, emphasizing photovoltaics. Between 2022 and 2023, installed photovoltaic power increased from 30.4 GW to 34.5 GW. Australian homeowners particularly benefit from incentive programs such as the Small-scale Renewable Energy Scheme (SRES), which makes installing solar systems at home very attractive. These initiatives support strong demand and promote expansion, despite the challenges the country faces in grid integration and reliance on imported technology.
The achievements of both countries are supported by their government support measures, but they prioritize different areas. While Spain’s strategy promotes a balanced mix of photovoltaic and solar thermal solutions, Australia decisively focuses on photovoltaics to meet individual needs. Both approaches demonstrate that government support and strategic development plans play essential roles in the expansion of renewable energies. The balance between growth and challenges is a common thread through the solar political efforts of both nations, allowing for notable progress in light of installed capacities and political objectives.