In the global financial circus, the S&P 500 and MSCI World are the ringmasters attracting investors with their unique characteristics. While the S&P 500 dominates the scene of the U.S. economy, the MSCI World draws attention with its international variety. This study explores the performance of these indices and how their diversification strategies influence risk for investors. Each chapter delves into the heart of these financial heavyweights and offers clear insights for investors choosing between a national focus and global dispersion.
Comparative Performance Analysis: S&P 500 vs. MSCI World Index
The two stock indices, S&P 500 and MSCI World Index, serve as benchmarks for investors keeping an eye on both U.S. and global stock markets. It may seem that the innovative power of the U.S. economy contrasts with a broader international spectrum. But what are the differences in performance for investors that result from this?
Composition and Coverage:
The S&P 500 captures the performance of the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the United States, dominating about 80% of the market capitalization of the U.S. stock market. Technology companies play a key role, with industry leaders like Apple and Microsoft at the top. In contrast, the MSCI World Index offers a broader coverage, including around 1,500 large and mid-sized companies from 23 developed markets worldwide. Although it has a global setup, about 70% of its weight is still represented by American companies, underscoring the dominance of the U.S. economy.
Performance Comparison:
Historically, the MSCI World Index has reported an average annual return of about 10.4% since 1978, making it a solid long-term investment class. However, particularly noteworthy is the superiority of the S&P 500 since 2008, with average annual returns of around 11.9%. This difference reflects the strength of the U.S. markets, especially in the technology sector. It is important to note, however, that international markets, as represented by the MSCI EAFE index, have been showing strong recent returns, while the S&P 500 has faced challenges lately.
Volatility Considerations:
In volatility analysis, it shows that the S&P 500, due to its focus on technology, tends to experience more volatile movements. Currently, the volatility of the SPDR S&P 500 ETF is at 5.70%, while the iShares MSCI ACWI ETF appears slightly more stable at 5.22%. These volatility differences highlight the risks and opportunities associated with focusing on technology-heavy markets compared to globally diversified investments.
Ultimately, the decision between the S&P 500 and the MSCI World Index heavily depends on individual investment strategies. The S&P 500 potentially offers greater growth opportunities due to the innovative power of American companies, while the MSCI World provides investment security through its geographical diversification.
Global Perspectives: S&P 500 vs. MSCI World in Terms of Diversification and Risk
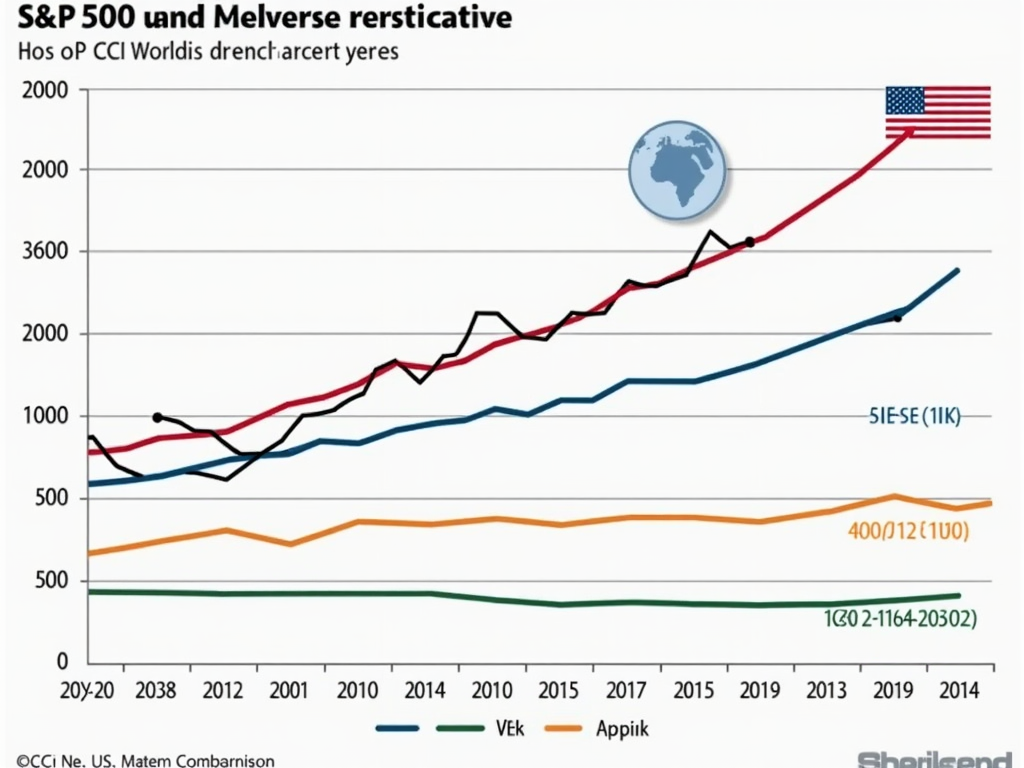
In the world of stock investments, the S&P 500 and the MSCI World play significant roles when it comes to diversification and risk. While the S&P 500 focuses solely on U.S. markets, the MSCI World opens the portfolio to a mix of global markets. But how does each of these indices actually perform in terms of risk and diversification?
Diversification
The S&P 500 offers diversification within the boundaries of the U.S. economy. With its 500 companies covering heavy industry, technology, health, and other sectors, it seems diversified at first glance. However, the reality shows a significant concentration: the ten largest companies represent about 37% of the index, which concentrates risks, especially during market periods sensitive to economic and technological cycles.
In contrast, the MSCI World spans around 1,600 companies from over 20 developed markets. Although it seems to provide a broader spread, the predominance of U.S. companies at about 60-73% is notable. The MSCI World also fails to completely free itself from dependence on U.S. market conditions. However, the inclusion of companies from regions like Europe and Japan simultaneously offers a chance of protection against fluctuations in the U.S. market.
Risk
Both indices are not without risks. The S&P 500 is heavily influenced by geopolitical tensions and U.S. economic conditions. The recent high weighting of technology companies brings the risk of a downturn during times of political or technological changes.
The same applies to the MSCI World. Although it is geographically well distributed, the dependence on the United States represents a risk that could weigh on the index in times of political tensions or economic recessions. Despite the diversification through international inclusion, the MSCI World remains particularly vulnerable when American tech giants are under pressure.
Risk Reduction Strategies
Investors are consistently seeking ways to reduce risk and strengthen portfolios. One approach is to diversify portfolios with more specific regional indices, such as the MSCI Europe. Commodities could also serve as a protective option, offering an alternative investment that can respond independently to fluctuations in the stock market.
Ultimately, it is essential to actively manage and respond to market movements. Portfolio adjustments or the use of derivatives can help keep risk under control.
The choice between the S&P 500 and MSCI World therefore heavily depends on individual risk tolerances and investor objectives, with both options presenting advantages and disadvantages in terms of diversification and risk.